在PyTorch中,有几种不同的工具可以用于网络结构的可视化。下面将以ResNet-18为例,展示如何使用常用的PyTorch画图工具进行网络结构的可视化。
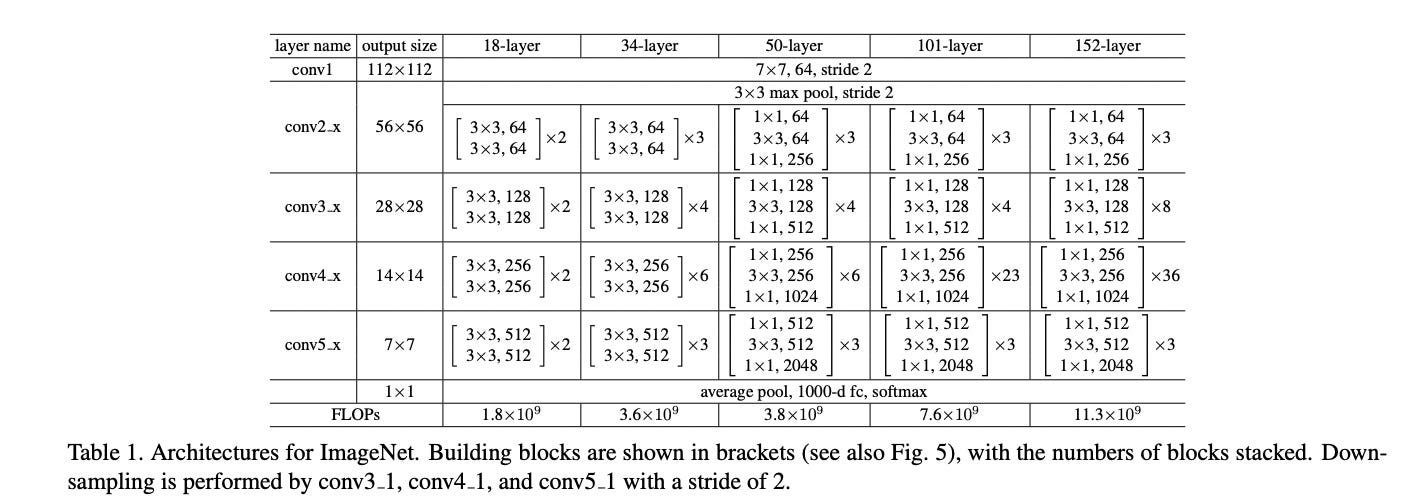
ResNet-18是一个经典的卷积神经网络模型,由多个卷积层、池化层、全连接层和残差连接(Residual Connection)组成。参考Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition,网络结构如下:
在PyTorch中可以能过torchvision快速使用ResNet-18,使用代码如下:
from torchvision.models import resnet18
x = torch.randn(1, 3, 224, 224)
model = resnet18()x是随机生成的输入数据,model是resnet18的实例。
1. torch print
使用torch自带的print方法。torch的model支持直接print打印,可以看到详细的网络结构。
使用示例:
print(model)结果如下:
ResNet(
(conv1): Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=(7, 7), stride=(2, 2), padding=(3, 3), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm2d(64, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(relu): ReLU(inplace=True)
(maxpool): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
(layer1): Sequential(
(0): BasicBlock(
(conv1): Conv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm2d(64, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(relu): ReLU(inplace=True)
(conv2): Conv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm2d(64, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
)
(1): BasicBlock(
(conv1): Conv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm2d(64, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(relu): ReLU(inplace=True)
(conv2): Conv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm2d(64, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
)
)
......2. torchsummary
代码库:https://github.com/sksq96/pytorch-summary
使用torchsummary进行model的打印,展示的信息比print会多出来参数量和shape信息
安装:
pip install torchsummary使用示例:
from torchsummary import summary
summary(model, x.squeeze(dim=0).shape)结果如下:
----------------------------------------------------------------
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
================================================================
Conv2d-1 [-1, 64, 112, 112] 9,408
BatchNorm2d-2 [-1, 64, 112, 112] 128
ReLU-3 [-1, 64, 112, 112] 0
MaxPool2d-4 [-1, 64, 56, 56] 0
Conv2d-5 [-1, 64, 56, 56] 36,864
BatchNorm2d-6 [-1, 64, 56, 56] 128
ReLU-7 [-1, 64, 56, 56] 0
Conv2d-8 [-1, 64, 56, 56] 36,864
BatchNorm2d-9 [-1, 64, 56, 56] 128
ReLU-10 [-1, 64, 56, 56] 0
BasicBlock-11 [-1, 64, 56, 56] 0
Conv2d-12 [-1, 64, 56, 56] 36,864
BatchNorm2d-13 [-1, 64, 56, 56] 128
ReLU-14 [-1, 64, 56, 56] 0
Conv2d-15 [-1, 64, 56, 56] 36,864
BatchNorm2d-16 [-1, 64, 56, 56] 128
ReLU-17 [-1, 64, 56, 56] 0
BasicBlock-18 [-1, 64, 56, 56] 0
Conv2d-19 [-1, 128, 28, 28] 73,728
BatchNorm2d-20 [-1, 128, 28, 28] 256
ReLU-21 [-1, 128, 28, 28] 0
Conv2d-22 [-1, 128, 28, 28] 147,4563. torchviz
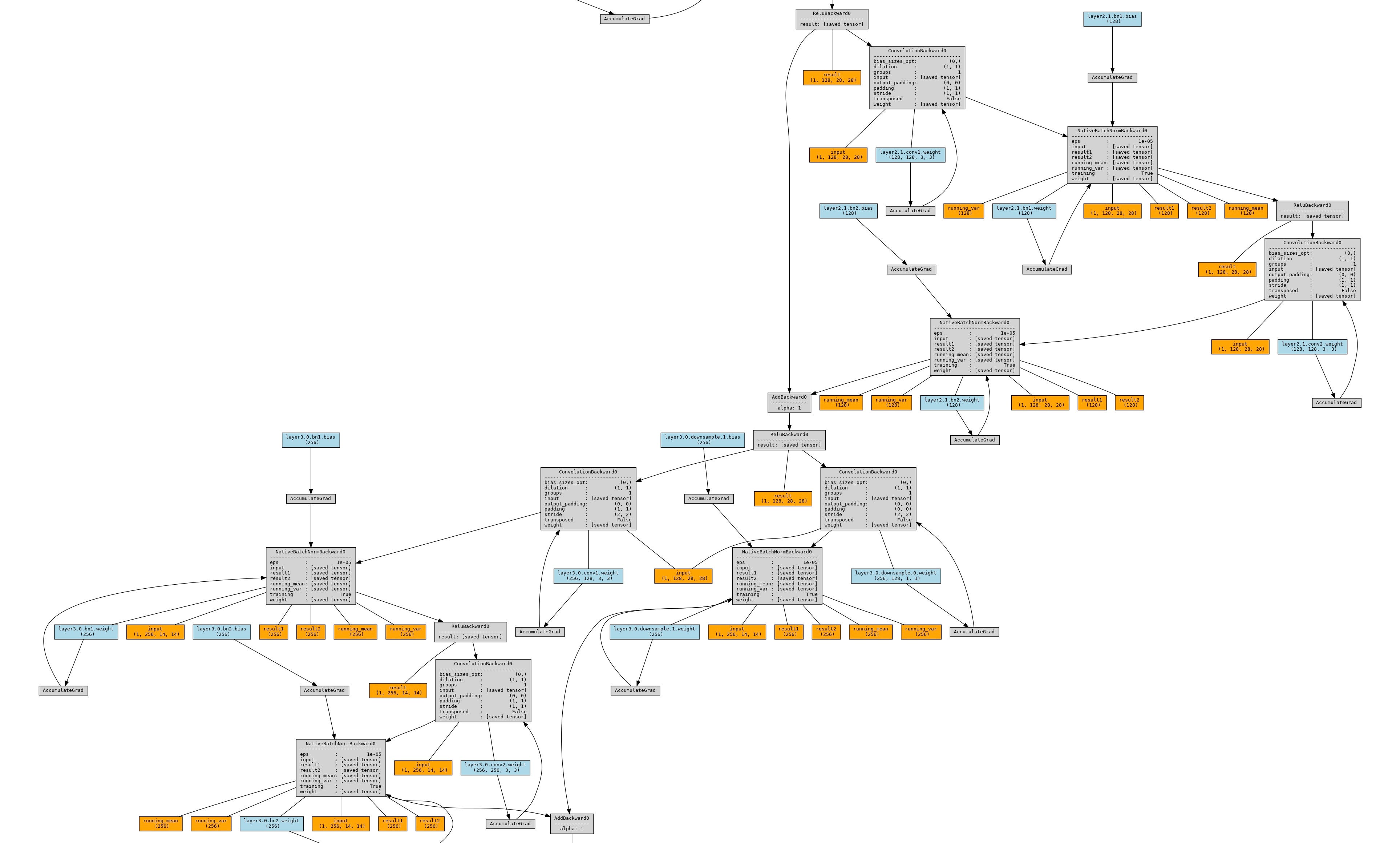
代码库:https://github.com/szagoruyko/pytorchviz
使用torchviz进行可视化(需要安装torchviz和graphviz)。torchviz会通过backward的过程对整个网络进行展示。
安装:
apt install python3-pydot python3-pydot-ng graphviz xdg-utils
pip install torchviz使用示例, 保存图片到文件中,如果终端直接展示的话render函数中的view配置改为True:
from torchviz import make_dot
y = model(x)
output = make_dot(y.mean(), params=dict(model.named_parameters()), show_attrs=True, show_saved=True)
output.format = "png"
output.directory = "."
output.render("torchviz", view=False)结果如下:
4. hiddenlayer
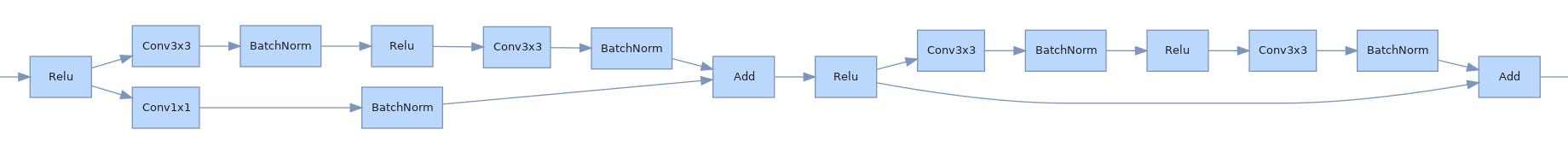
代码库:https://github.com/waleedka/hiddenlayer
hiddenlayer跟之前比的一个特色在于,hiddenlayer中支持transforms配置,可以对指定的多个连续算子进行fusion展示,以及有多个重复的结构的话可以进行fold压缩展示。
安装:
pip install matplotlib
pip install hiddenlayer使用示例:
import hiddenlayer as hl
transforms = [
# Fold repeated blocks
hl.transforms.FoldDuplicates(),
]
graph = hl.build_graph(model, x, transforms=transforms)
graph.theme = hl.graph.THEMES['blue'].copy()
graph.save('hiddenlayer', format='png')结果如下:
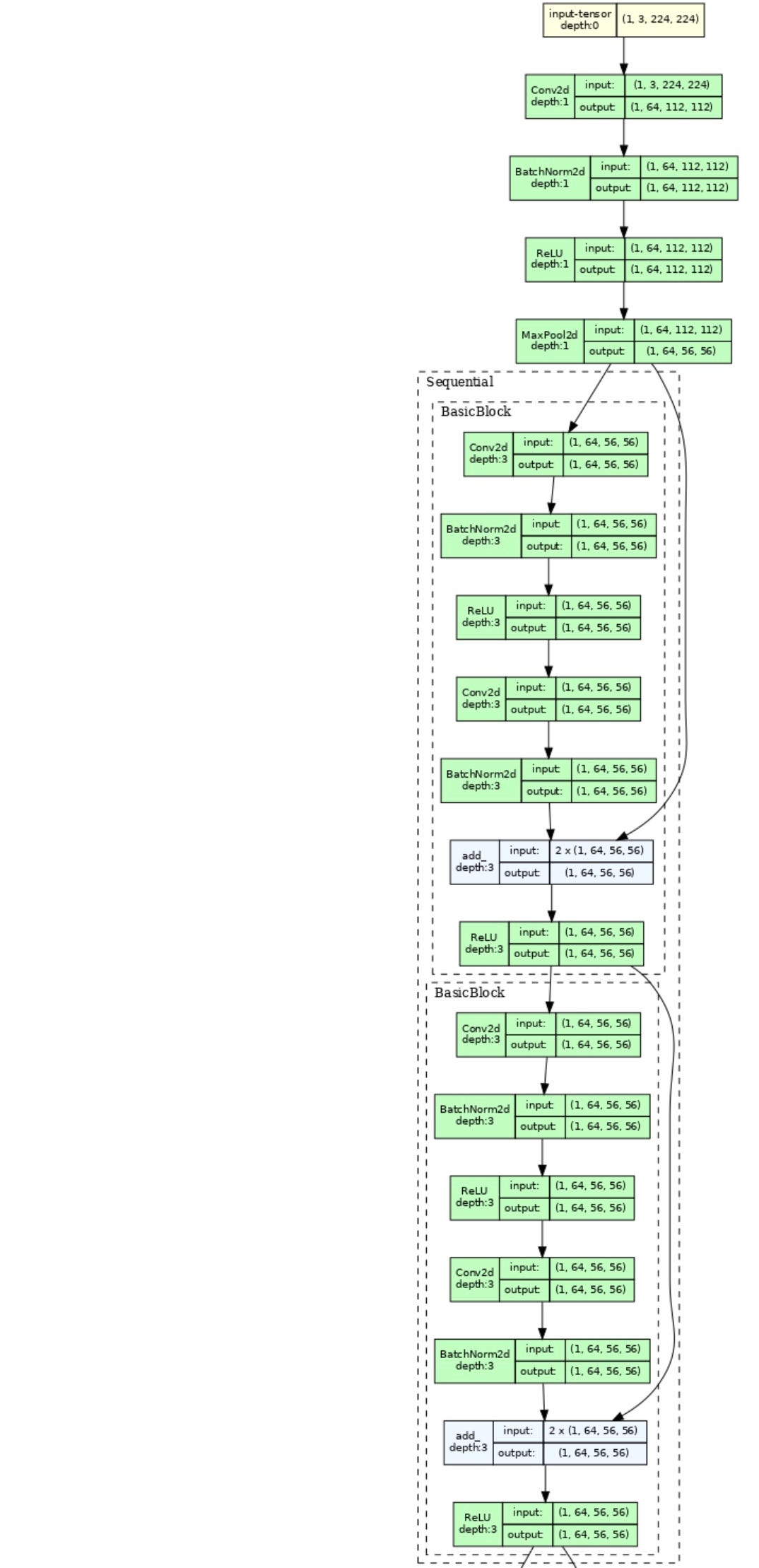
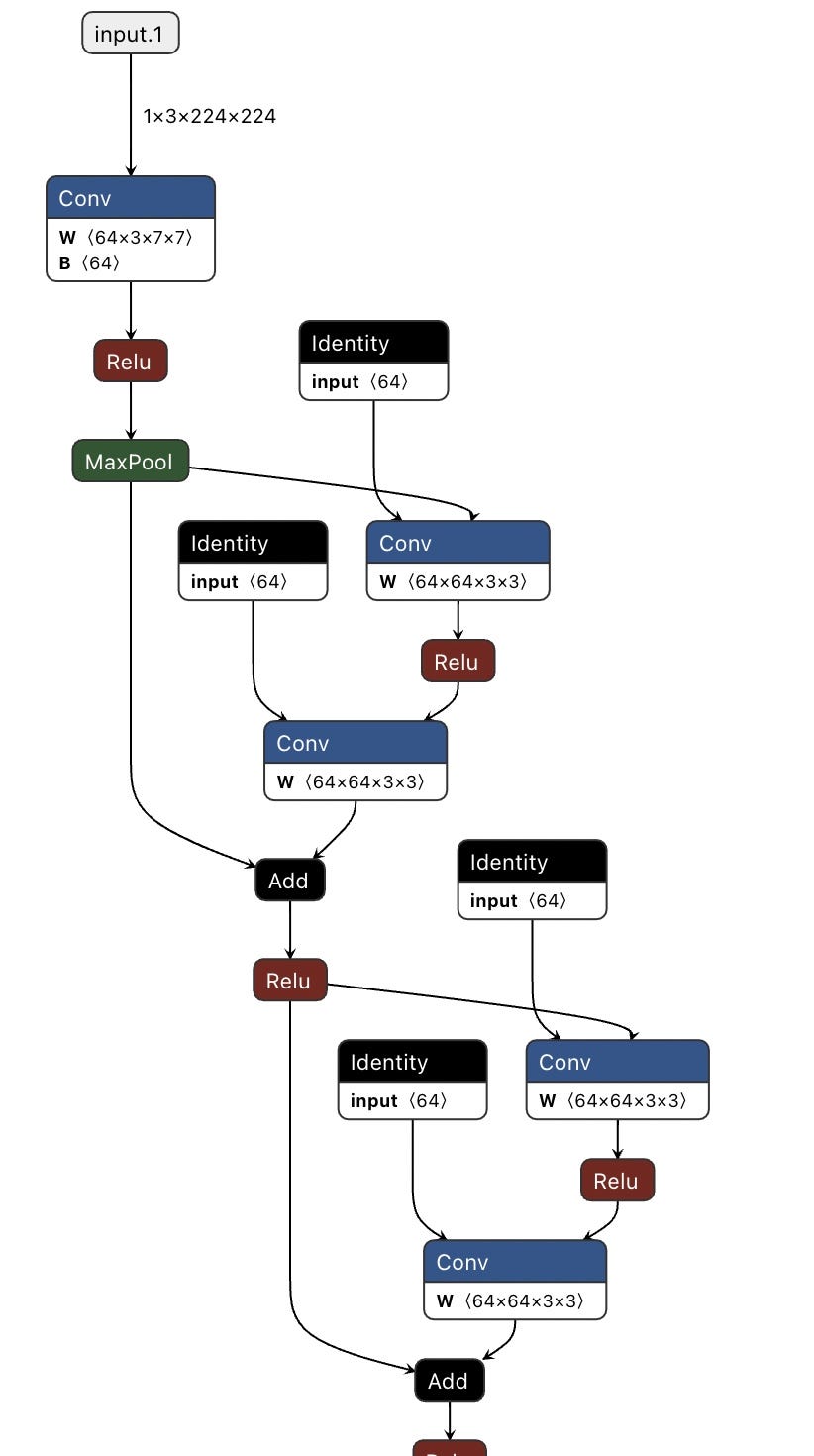
5. torchview
代码库:https://github.com/mert-kurttutan/torchview
安装:
pip install torchview使用示例:
from torchview import draw_graph
model_graph = draw_graph(model, input_size=x.shape, expand_nested=True, save_graph=True, filename="torchview", directory=".")
model_graph.visual_graph结果如下:
6. netron
代码库:https://github.com/lutzroeder/netron
netron可以对保存的模型文件进行可视化展示。介绍中支持的格式有:
Netron supports ONNX, TensorFlow Lite, Caffe, Keras, Darknet, PaddlePaddle, ncnn, MNN, Core ML, RKNN, MXNet, MindSpore Lite, TNN, Barracuda, Tengine, CNTK, TensorFlow.js, Caffe2 and UFF.
安装:
pip install onnx
pip install netron使用示例:
onnx_file_path = "resnet18.onnx"
torch.onnx.export(model, x, onnx_file_path, verbose=True)使用netron导入resnet18.onnx文件,结果如下:
7. 完整代码
#!/usr/bin/env python
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torchvision.models import resnet18
def draw_torchsummary(model, x):
from torchsummary import summary
summary(model, x.squeeze(dim=0).shape)
def draw_torchviz(model, x):
from torchviz import make_dot
y = model(x)
output = make_dot(y.mean(), params=dict(model.named_parameters()), show_attrs=True, show_saved=True)
output.format = "png"
output.directory = "."
output.render("torchviz", view=False)
def draw_torchview(model, x):
from torchview import draw_graph
model_graph = draw_graph(model, input_size=x.shape, expand_nested=True, save_graph=True, filename="torchview", directory=".")
#model_graph.visual_graph
def draw_hiddenlayer(model, x):
import hiddenlayer as hl
transforms = [
# Fold repeated blocks
hl.transforms.FoldDuplicates(),
]
graph = hl.build_graph(model, x, transforms=transforms)
graph.theme = hl.graph.THEMES['blue'].copy()
graph.save('hiddenlayer', format='png')
def draw_netron(model, x):
onnx_file_path = "resnet18.onnx"
torch.onnx.export(model, x, onnx_file_path, verbose=True)
if __name__ == "__main__":
x = torch.randn(1, 3, 224, 224)
model = resnet18()
print(model)
draw_torchsummary(model, x)
draw_torchviz(model, x)
draw_hiddenlayer(model, x)
draw_torchview(model, x)
draw_netron(model, x)